Building a Centralized IAM and Permission Set Management Framework in AWS
Published on November 22, 2025
Managing user access and permissions across multiple AWS accounts is one of the most critical—and challenging—parts of cloud governance.
In this post, we’ll walk through how we designed and implemented a centralized AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Permission Set framework, integrated with AWS Identity Center (formerly SSO) and Active Directory, along with a Jenkins pipeline for automated policy deployment.
Problem Statement
As the AWS environment grows (multiple accounts such as Prod, Pilot, UAT, Shared, etc.), manual IAM management becomes error-prone and inconsistent.
Common challenges include:
- Inconsistent IAM policies across accounts
- Manual updates in the AWS console
- Lack of audit trail and deployment automation
- Delayed provisioning and removal of user access
Solution Overview
To solve this, we built a Centralized IAM and Permission Set Management Framework consisting of:
- AWS Identity Center for unified authentication and role-based access
- Customer Managed IAM Policies for granular permissions
- Permission Sets mapped with AD groups
- Jenkins pipeline integrated with Git for automated deployment
This design ensures security, consistency, and compliance across all AWS environments.
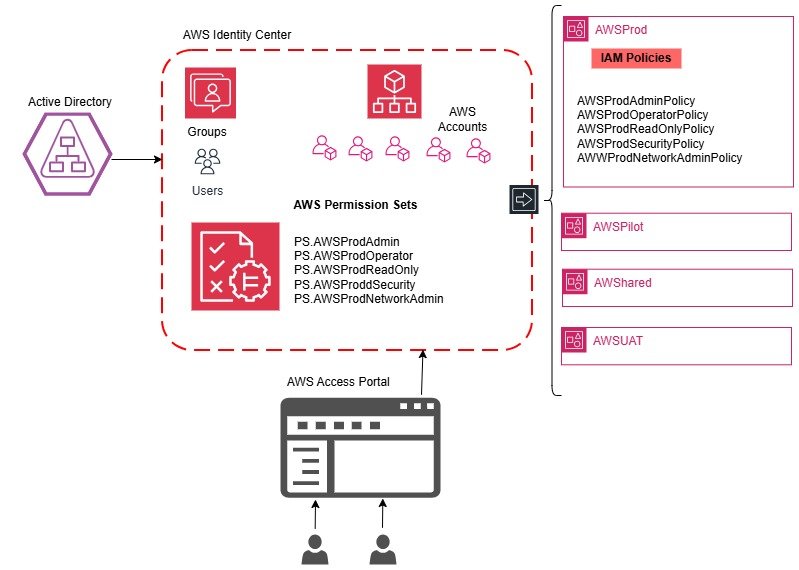
AWS Accounts
framework covers multiple AWS accounts:
AWSProd
AWSPilot
AWSUAT
AWSSharedProdEach account holds customer-managed IAM policies and is linked to AWS Identity Center.
AWS Identity Center Integration
AWS Identity Center acts as the single source of truth for authentication and authorization.
It connects with Active Directory for user management and uses Permission Sets for role-based access control.
Key highlights:
- SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management) automates user and group provisioning.
- SAML provides single sign-on authentication.
- Each Permission Set defines the IAM policies attached, mapped to corresponding AD groups.
IAM Policy Centralization
All IAM policies are stored in a Git Repository.
Each JSON file defines a customer-managed IAM policy, version-controlled for traceability.
Sample naming:
AWSProd
AWSPilot
AWSUAT
AWSSharedProdEach account holds customer-managed IAM policies and is linked to AWS Identity Center.
IAM Policy Centralization
All IAM policies are stored in a Git Repository.
Each JSON file defines a customer-managed IAM policy, version-controlled for traceability.
Sample naming:
AWSProdAdminPolicy.json
AWSProdOperatorPolicy.json
AWSProdReadOnlyPolicy.json
AWSProdInfoSecPolicy.json
AWSProdNetworkAdminPolicy.jsonAutomated Deployment using Jenkins
We implemented a Jenkins pipeline to automatically:
- Detect changed policy JSON files in Git
- Validate JSON syntax & size (IAM policy limit = 6144 bytes)
- Create or update the IAM policy in the target AWS account
- It also includes a manual approval stage before deployment.
Architecture Diagram
Conclusion
By implementing a centralized IAM and Permission Set governance model, teams can streamline user access management, maintain compliance, and eliminate human error.
Combined with CI/CD automation, this framework serves as a scalable, secure, and efficient foundation for multi-account AWS environments.